Manufacturing Process
[1] RAW MATERIALS
The first step is to weigh
[2] MIXING
Dry mix and ball mill the raw materials
[3] Calcining
The uniform mixture is then heat treated (calcined) during which the components react to form the polycrystalline phase
[4] MILLING
[5] SPRAY DRYING
The calcined powder is spray dried to add binder in order to increase it's reactivity and to improve pressing properties.
[6] PRESSING
Shaping by dry-pressing

[7] BINDER BURNOUT
The binder is burnt out by slowly heating the green ceramics to around 700oC
[8] SINTERING
The parts are transferred to another furnace, where they are sintered between 1200oC and 1300oC
[9] GRINDING / POLISHING
The dimensional tolerance of fired parts is improved by cutting, grinding, lapping etc.
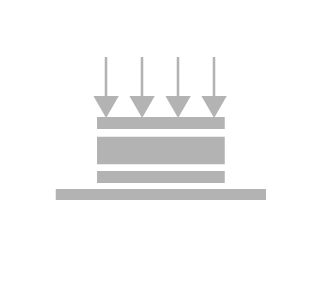
[10] ELECTRODING
Electrodes are applied either by screen printing, chemical plating or vacuum deposition
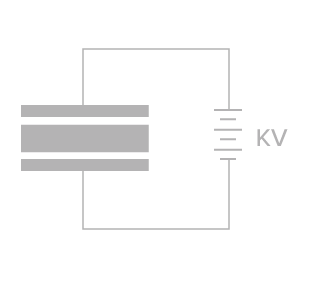
[11] POLING
Poling then is carried out by heating in an oil bath above Curie Temperature, and applying an electrical field of 2-8 kV/mm to align the domains in the material.

[12] FINAL INSPECTION
Final inspection is performed after a minimum of 24 hours later, and includes testing of electrode-ceramic bonding as well as measurement of dimensional tolerances, dielectric and piezoelectric properties.

